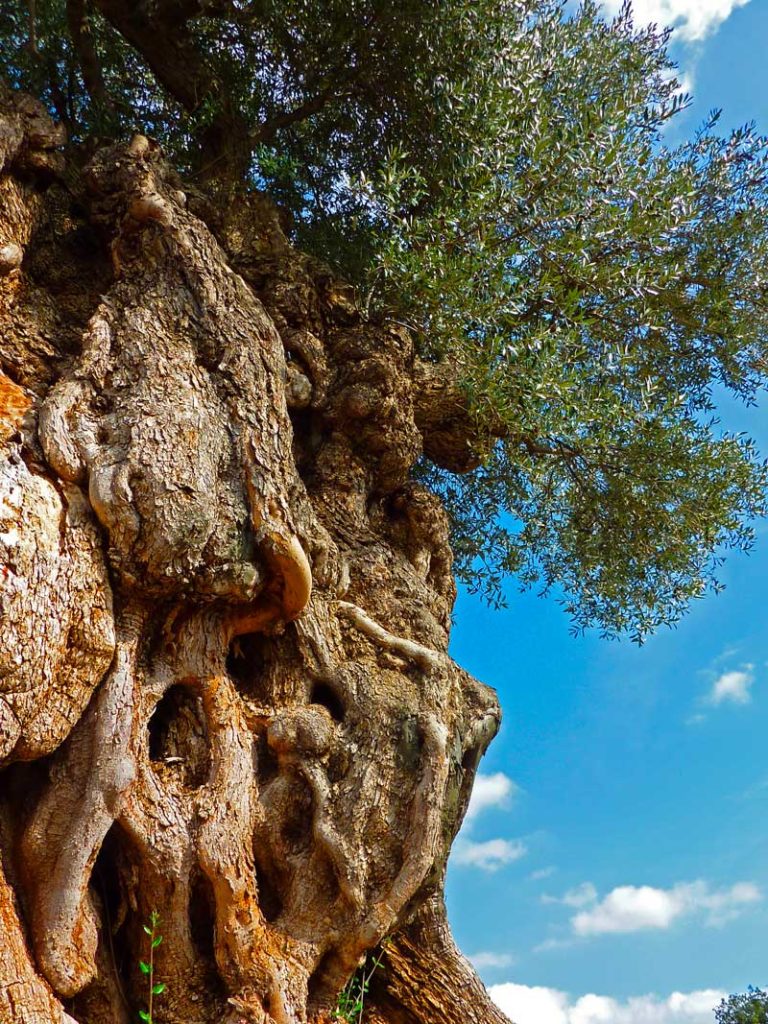
The history of the olive tree began in Greece, 37,000 years before our era. It survived the last glacial period and developed from a bush, the wild-olive. In France, olive trees have been part of the Mediterranean landscape for 7000 years.
There are 830 million olive trees all over the world, with 90% of them in the Mediterranean area.
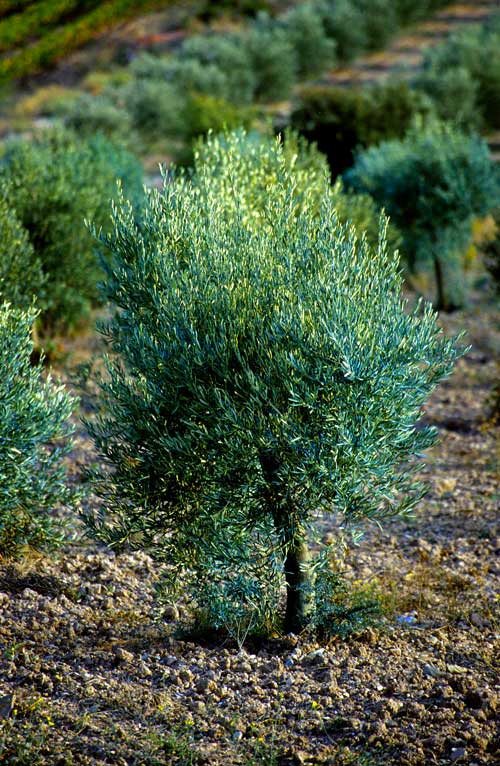
The tree is typically found in garrigue (heath) areas. It is resistant to drought but is sensitive to frost. It can grow even in the poorest soils, including stony ground, and its roots can reach down 6 metres for water.
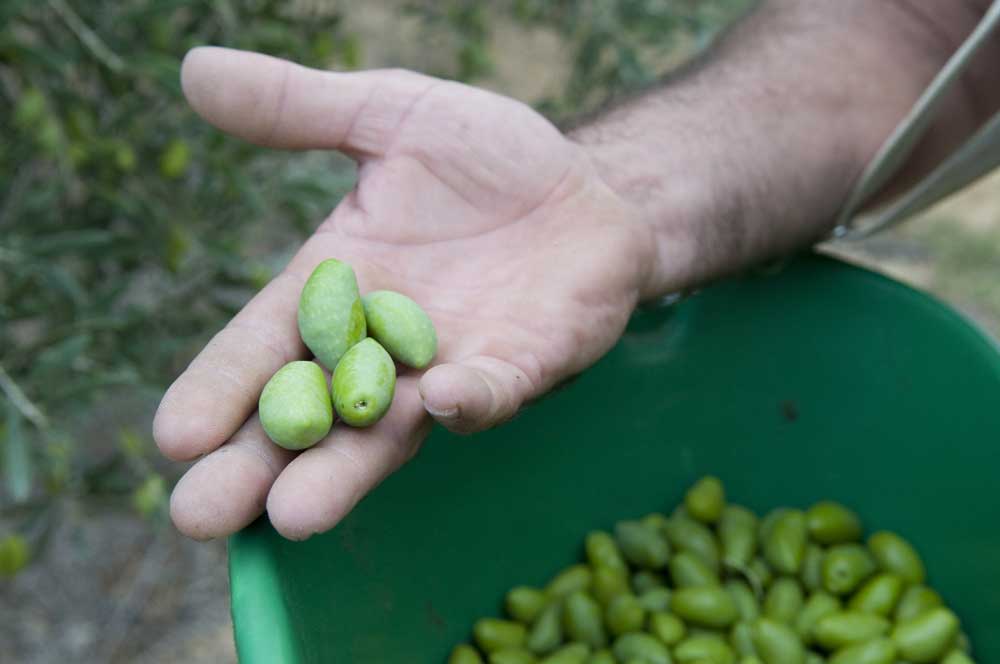
Olive trees grow slowly. The first olives appear when the tree is between 3 and 7 years old (depending on the variety). An olive tree reaches full maturity after 10 years and starts to decline in fertility after about 150 years. In favourable conditions, they can live up to one thousand years.